Kramers' law
Kramers' law is a formula for the spectral distribution of X-rays produced by an electron hitting a solid target. The formula concerns only bremsstrahlung radiation, not the element specific characteristic radiation. It is named after its discoverer, the Dutch physicist Hendrik Anthony Kramers[1].
The formula for Kramers' law is usually given as the distribution of intensity vs. the wavelength of the emitted radiation:[2]
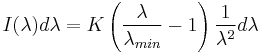
The constant K is proportional to the atomic number of the target element.
References
- ^ Kramers, H.A. (1923). Phil. Mag. 46: 836.
- ^ Laguitton, Daniel; William Parrish (1977). "Experimental Spectral Distribution versus Kramers' Law for Quantitative X-ray Fluorescence by the Fundamental Parameters Method". X-ray Spectrometry 6 (4): 201. doi:10.1002/xrs.1300060409.